We are thrilled to announce the official launch of our new website, Polar Latitudes Expeditions. Discover more in our latest news update, and visit our new website polar-latitudes.com.
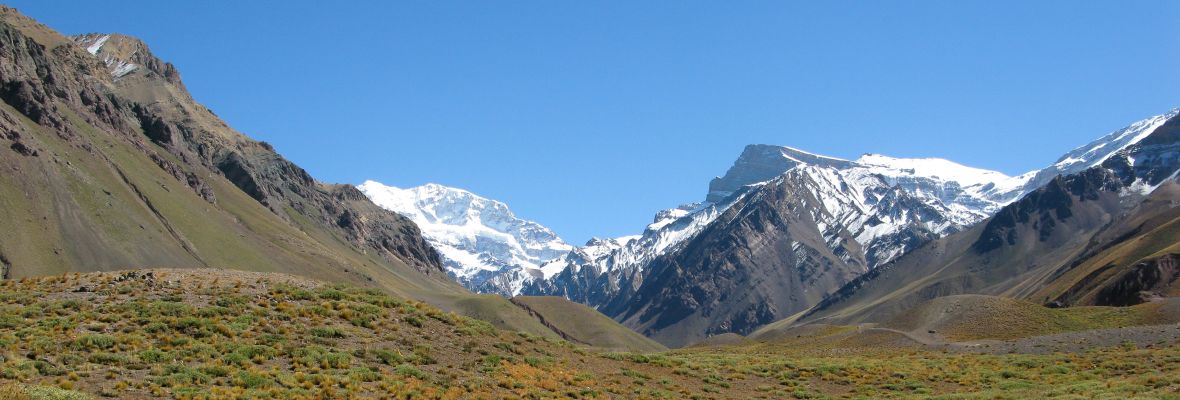
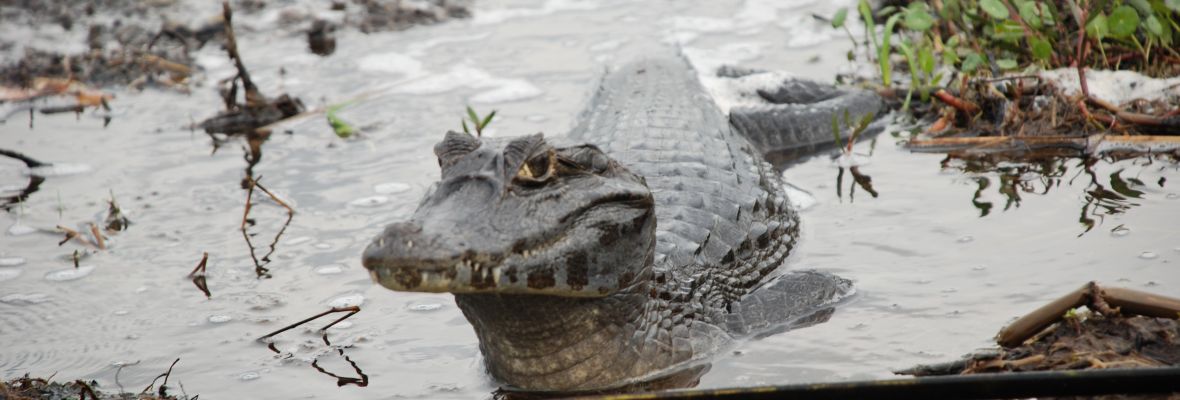
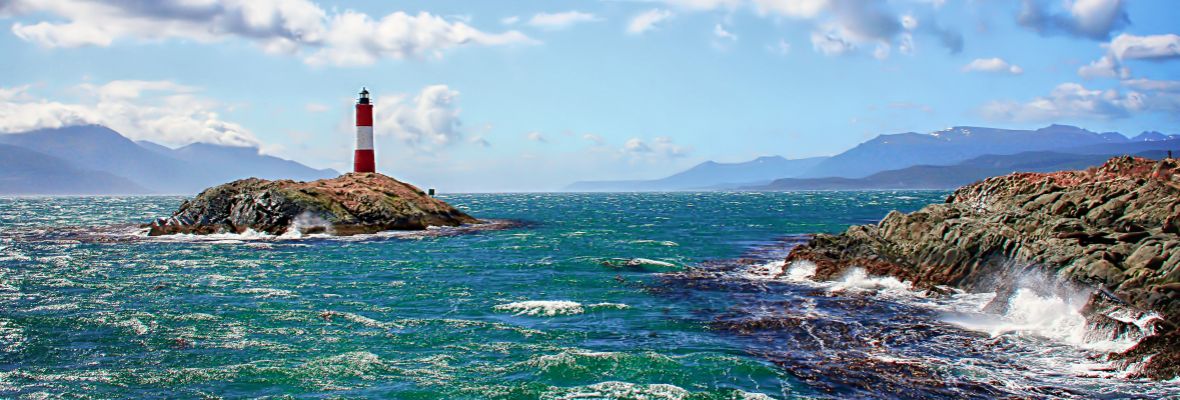
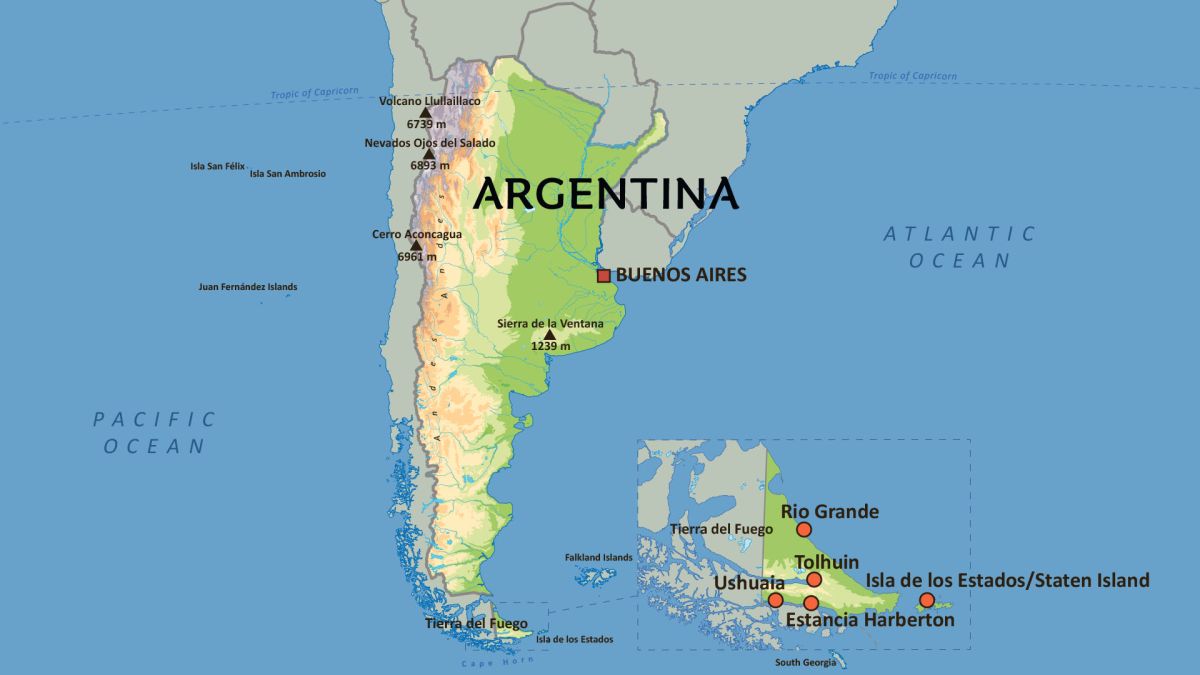
Argentina’s vast and varied geography hosts an incredibly diverse range of ecosystems, making it one of the most biodiverse countries in the world.
Argentina is divided into six distinct geographical regions, each with its own unique climate, wildlife, and landscapes. These regions are: the Argentine Northwest, Gran Chaco and Mesopotamia in the north; Cuyo in the west; the Pampas in the center and East; and Patagonia in the south.
Facts about Geography and Map of Argentina
- South America
- Argentina