Exciting changes are on the way!
As part of our merger with Polar Latitudes, we’re refreshing key elements of our website to reflect this new chapter. Discover more in our latest news update.
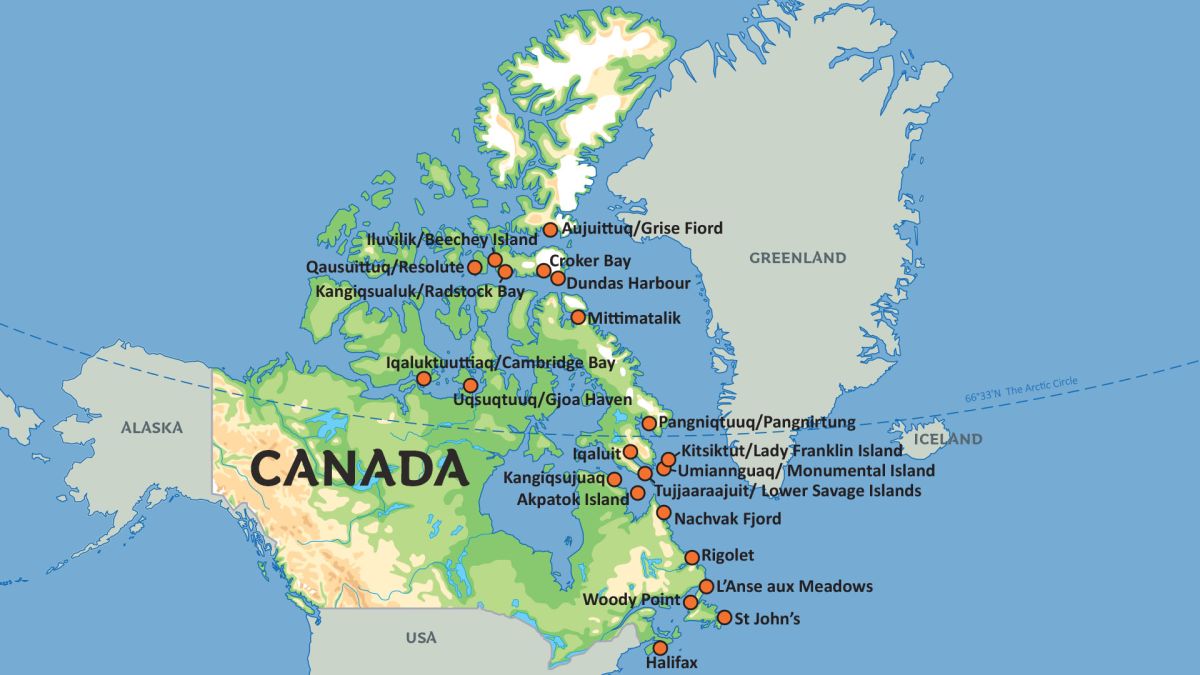
Arctic Canada is characterized by its landscapes, which are shaped by ice, wind, and extreme temperatures. It includes coastal plains, ice fields, and thousands of islands that stretch toward the North Pole.
Arctic Canada is a huge territory covering nearly 40% of the country’s total landmass, and includes the northernmost regions of the Canadian mainland as well as the Arctic Archipelago. This region is mostly a tundra biome with glaciers and permafrost, much of the land is frozen year-round.
Facts about Map and Geography of Arctic Canada
- Arctic
- Canada